
With the Umar Khalid and Sharjeel Imam cases once again drawing global attention, especially after Umar Khalid’s father met US politician Zohran Mamdani, it’s the right time to scrutinize why the Supreme Court rejected bail pleas for both activists. The issue has sparked renewed discussion around India’s anti-terror law, the UAPA, and how it is applied in high-profile cases.
In the age of social media, misinformation often travels across the world long before the truth gets its moment. That makes it all the more important to examine each argument carefully and understand the reasoning behind the court’s responses. We are living in a time where selective fact-checking is common, misinformation is circulated to serve political agendas, and inconvenient truths are pushed out of sight. From what I have seen, some of the material relevant to this case has still not reached the wider public because it is rarely covered by mainstream media. As a result, distrust continues to linger.
Of course, for some people, no amount of truth really matters. What they seek is validation for their existing biases or political leanings. This post is not meant for that audience. No amount of proof can change such a mindset. It is written for readers willing to acknowledge facts when presented.
Getting back to the case, according to the prosecution, Umar Khalid and Sharjeel Imam were not just participants but masterminds who mobilised or influenced others during the events in question. The defence, however, put forward two key arguments while seeking their release on bail. Let’s take a closer look at what those arguments were and why the court chose not to accept them.
Defense Argument #1:
Not Directly Involved in Violence

One of the most repeated arguments, especially in Umar Khalid’s case, is that he was not present at the riot spots when the violence took place.
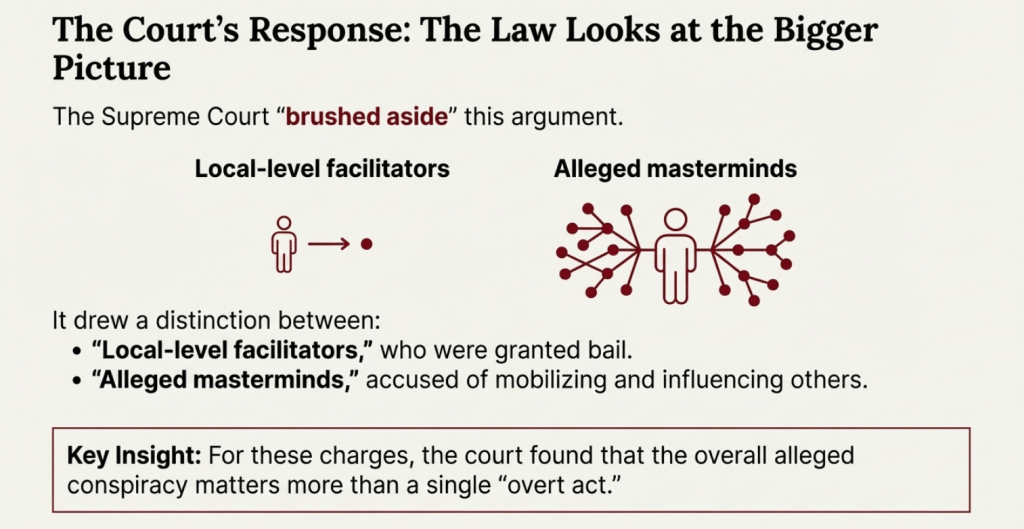
Court Response
The court indicated that the act of masterminding the riots, even without direct presence, was in itself sufficient. The court’s position was clear and firm: nothing comes above the interests of national security. On a prima facie assessment of the material placed before it, which includes videos, audios, posts, and messages, the court held that both Umar Khalid and Sharjeel Imam faced similar allegations of being the masterminds, which weighed heavily against granting bail. Due to their involvement in the larger plan, several people were killed and injured, including an intelligence officer.
It should be noted that provocative words alone can be enough to incite violence. This is not something new. Something similar was seen even before the Gujarat riots, where RSS members were found to have mobilised people through provocative speeches. Many who provoked never participated in the violence, but their words were enough. They were taken into custody and remained there for years.
This raises an important question: what makes those cases different from the cases of Sharjeel Imam and Umar Khalid, so that the latter deserves bail? Both instances were the same: provocative speeches leading to mass mobilization. The 2020 Delhi riots too had a communal angle, with tensions between different communities being stirred during the violence. Videos of the provocative communal speeches are available widely on X. WhatsApp groups were formed along religious lines, which added to the sense of division at the time.
Rather than relying on political influencers or commentators, I recommend reading the official case files to understand the facts as presented in court. You can find these by searching Google with terms like “Delhi NCT Sharjeel Imam pdf” and then looking within the document for specific details.
Often, religion is used as a tool to strengthen or manipulate one’s case, and that appears to have happened here as well. As someone who has gone through the provocative videos and social media posts of the two, it is difficult to see them as innocent. I cannot quote or reproduce those statements here because of their sensitive nature, but they are publicly available and can be found on social media platforms like X by searching their names.
Sharjeel Imam’s Facebook account is still active, while Umar Khalid has deleted his. I would recommend going through Sharjeel’s Facebook posts to see for yourself how passionately he tried to convince people to hit the streets. Some posts had a communal dimension as well. The content includes rhetoric that can be interpreted as calls for violence and even secession, which adds serious weight to the charges against them.
Defense Argument #2:
The Trial Delay
One more argument that often comes up is the long delay in the trials of Sharjeel Imam and Umar Khalid.

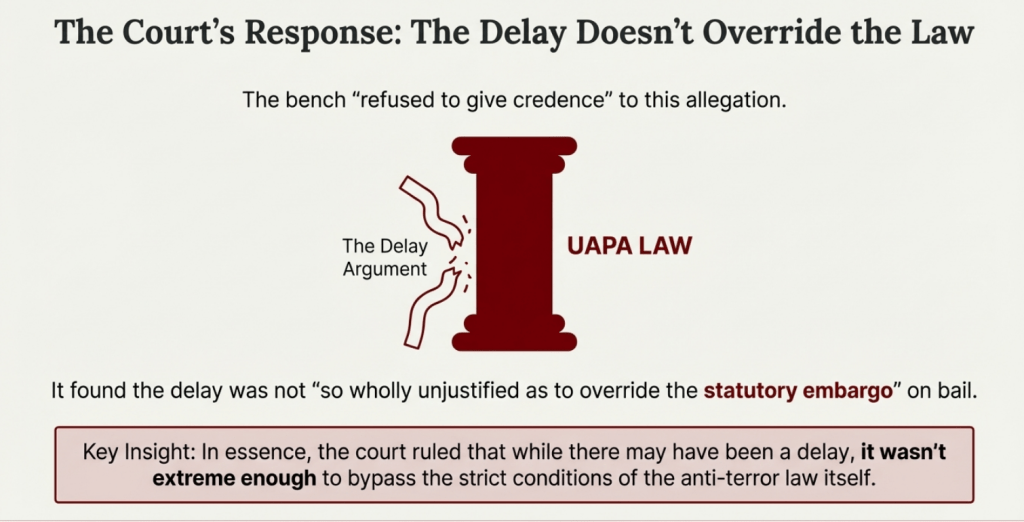
Court Response
The court maintained that a delay in the trial does not dilute the gravity of the case.
Also Read: CJI’s Remarks on Umar Khalid’s Trial Delays
The Final Verdict
The court observed that the polarising material appeared prima facie true, and this played a key role in denying bail to them as alleged masterminds.
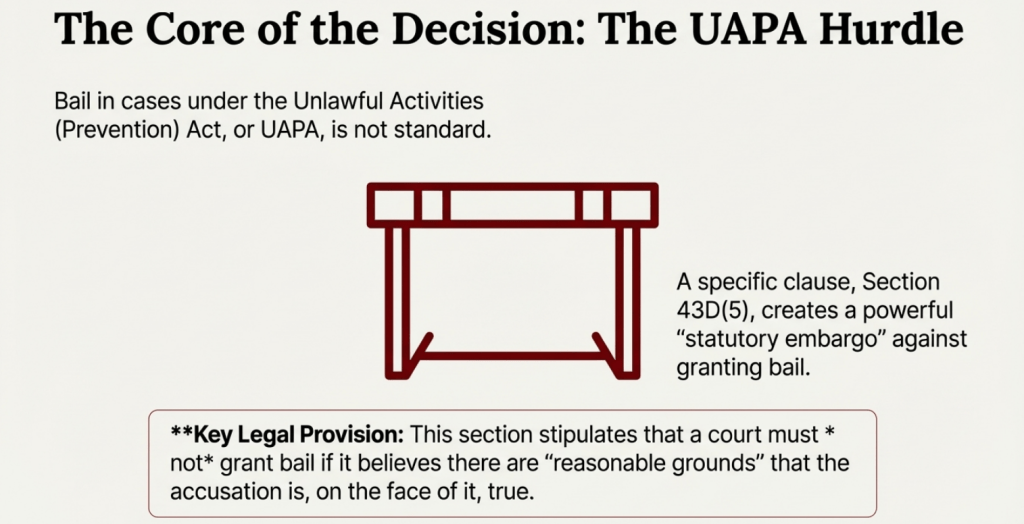

The court admitted that balancing individual rights with the nation’s security is never an easy task.
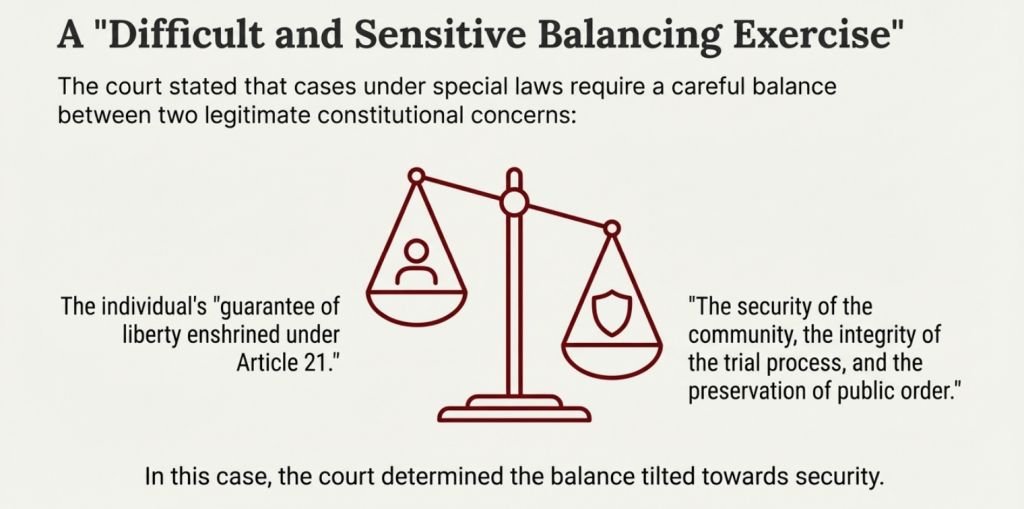


Umar Khalid and Sharjeel Imam were not denied bail because of unfairness or a failure of the legal system. Their bail was rejected because the court found the material presented before it to be valid and credible.
However, unless this material, such as videos or posts, is made available for public viewing in a structured and responsible manner, many people will continue to believe that the legal system itself is fractured. Since I have seen the provocative videos and social media posts and gone through the case details, I do not doubt the court’s reasoning.
But the lack of transparency leaves room for misunderstanding. It also creates space for political parties and interest groups to selectively present facts and shape narratives for their own benefit. Should there not be a mechanism to clearly explain why and how such decisions are taken, along with supporting material, so that the ordinary citizen does not have to rely on fragments found on their own?







You must be logged in to post a comment.